- We succeed where others fail!
- 860.564.7817
- Email Us
Prepreg Composite Materials
- Home
- Prepreg Composite Materials
Prepreg Composite Materials From APCM
Most commonly used by experienced fabricators, prepregs are high-performance materials that have been reinforced with a thermoplastic or thermoset resin. Typically, prepregs are more expensive than their dry fabric counterparts, but they’re imperative for applications where strength, weight, and stability cannot be compromised.
Prepreg Composite Materials
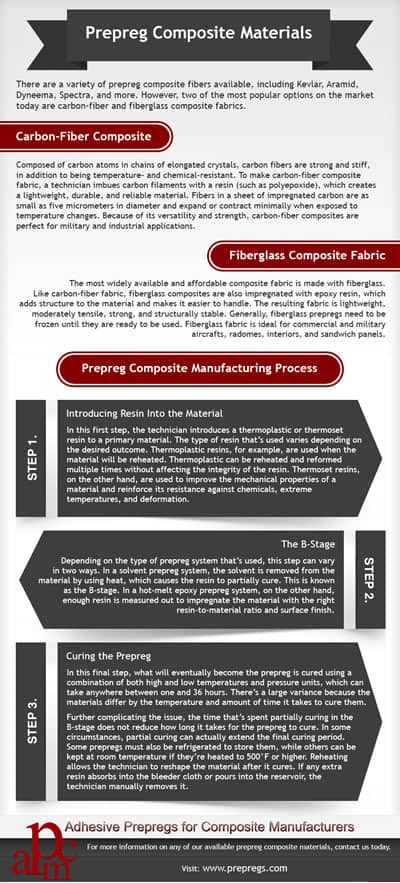
There are a variety of prepreg composite fibers available, including Kevlar, Aramid, Dyneema, Spectra, and more. However, two of the most popular options on the market today are carbon-fiber and fiberglass composite fabrics.
Carbon-Fiber Composite
Composed of carbon atoms in chains of elongated crystals, carbon fibers are strong and stiff, in addition to being temperature- and chemical-resistant. To make carbon-fiber composite fabric, a technician imbues carbon filaments with a resin (such as polyepoxide), which creates a lightweight, durable, and reliable material. Fibers in a sheet of impregnated carbon are as small as five micrometers in diameter and expand or contract minimally when exposed to temperature changes. Because of its versatility and strength, carbon-fiber composites are perfect for military and industrial applications.
Fiberglass Composite Fabric
The most widely available and affordable composite fabric is made with fiberglass. Like carbon-fiber fabric, fiberglass composites are also impregnated with epoxy resin, which adds structure to the material and makes it easier to handle. The resulting fabric is lightweight, moderately tensile, strong, and structurally stable. Generally, fiberglass prepregs need to be frozen until they are ready to be used. Fiberglass fabric is ideal for commercial and military aircrafts, radomes, interiors, and sandwich panels.Prepreg Composite Manufacturing Process
Prepreg composite materials are usually manufactured in three main steps: adding resin, partially curing, and then curing the prepreg.Step 1. Introducing Resin Into the Material
In this first step, the technician introduces a thermoplastic or thermoset resin to a primary material. The type of resin that’s used varies depending on the desired outcome. Thermoplastic resins, for example, are used when the material will be reheated. Thermoplastic can be reheated and reformed multiple times without affecting the integrity of the resin. Thermoset resins, on the other hand, are used to improve the mechanical properties of a material and reinforce its resistance against chemicals, extreme temperatures, and deformation.Step 2. The B-Stage
Depending on the type of prepreg system that’s used, this step can vary in two ways. In a solvent prepreg system, the solvent is removed from the material by using heat, which causes the resin to partially cure. This is known as the B-stage. In a hot-melt epoxy prepreg system, on the other hand, enough resin is measured out to impregnate the material with the right resin-to-material ratio and surface finish.Step 3. Curing the Prepreg
In this final step, what will eventually become the prepreg is cured using a combination of both high and low temperatures and pressure units, which can take anywhere between one and 36 hours. There’s a large variance because the materials differ by the temperature and amount of time it takes to cure them. Further complicating the issue, the time that’s spent partially curing in the B-stage does not reduce how long it takes for the prepreg to cure. In some circumstances, partial curing can actually extend the final curing period. Some prepregs must also be refrigerated to store them, while others can be kept at room temperature if they’re heated to 500°F or higher. Reheating allows the technician to reshape the material after it cures. If any extra resin absorbs into the bleeder cloth or pours into the reservoir, the technician manually removes it.Prepreg Composite Materials from APCM
Prepregs are ideal for situations where performance, weight, and mechanical properties are top priorities. They’re safe to use for a variety of applications. In general, they are environmentally cleaner and less toxic than other products that perform similar functions. Prepregs are also available in a variety of forms, including rolls, sheets, and pre-cut segments. Unless otherwise stated, all prepregs from APCM need to be refrigerated for 6 months or frozen for longer storage but have a cumulative out time of 30 days before they expire. With almost three decades of experience designing, manufacturing, and producing prepregs that are as light, strong, and fast as possible, APCM is the Northeast’s go-to provider of prepreg composite materials for manufacturers and hobbyists alike. For more information on any of our available prepreg composite materials, contact us today.
// Prepregs Products
APCM, LLC. the company, we help make our customers